LCMS & MALDI Newsletter - Spring 2021
Check out the latest customer interviews, and find out information on the state of the art instrument and software updates currently available from Shimadzu!
User Interviews
Instrumentation & Software News
Tackling Heart Disease using LCMS and MALDI Techniques
Professor Toru Suzuki, MD PhD FRCP FHEA, University of Leicester is chair of Cardiovascular Medicine and an honorary consultant cardiologist as well as the director of Leicester Life Sciences Accelerator and Associate Dean at the College of Life Sciences at University of Leicester.
Shimadzu has been a long-time collaborator of mine for proteomics and metabolomics investigations. I have been working with them on both LCMS and MALDI-TOF MS methods for almost twenty years now. Beginning with my work with them at the University of Tokyo where we started with the AXIMA CFR and the LCMS-8030. Through turnover of numerous generations of instruments and a move to the UK, I now use an AXIMA Confidence and an LCMS-8050 and LCMS-8060, and continue to use Shimadzu instruments and work closely with them. As an investigator and clinical academic of the MRC-funded UK Consortium on MetAbolic Phenotyping (MAP-UK) which aims to share the excellence in the UK on metabolomics, I contribute mainly to targeted methods for analysis of large cohorts. Shimadzu is supporting my lab on MAP-UK to progress/advance targeted analysis of metabolites and sharing protocols/methods with other groups.
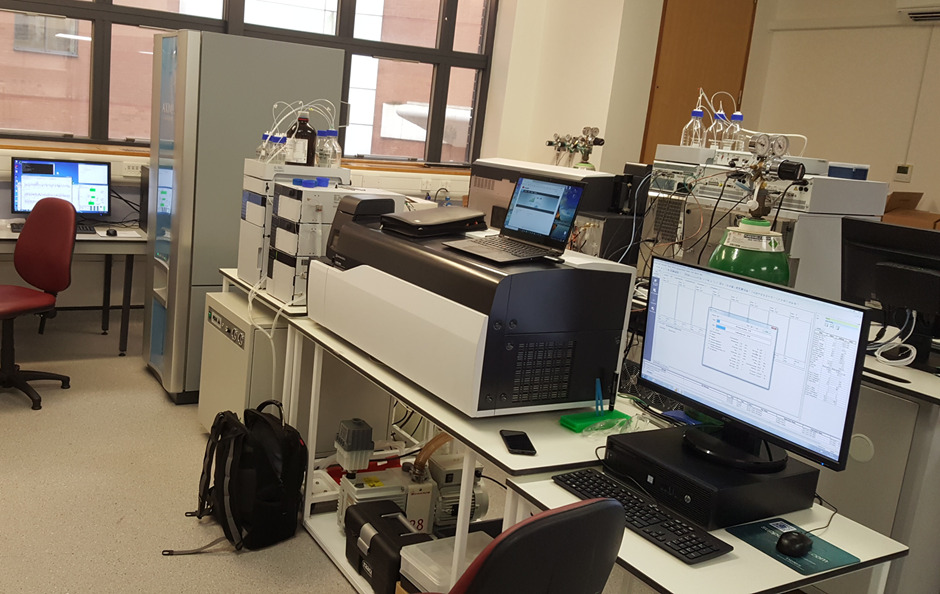

LCMS-8050 and LCMS-8060 in back-to-back configuration with AXIMA Confidence at the end.
My lab, as a representative project, characterised the role of the gut microbiome in heart disease, with a focus on the role of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a choline/carnitine metabolite that requires the gut microbiome for its production. We have characterised TMAO and related metabolites in heart failure and myocardial infarction among other heart diseases, as well as geographical
and ethnic differences. This research mainly uses the LCMS-8050 and LCMS-8060 triple quadruple MSs. As an oxidised lipid, this extends our understanding of how cholesterol through dietary egg yolk and red meat can affect your heart health/diseases with now a new dimension in our understanding through the contribution of the gut microbiome. This new 'gut-heart' axis adds to our understanding of mechanisms underlying heart disease.
MALDI-MS methods have been used to characterise the metabolic/processing of peptides, for instance in representative studies that have focussed on B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), a hormone produced in the heart to counteract heart failure and hemodynamic stress by inducing a natriuretic response. As with other hormones, processing/metabolism affects the bioactivity of this and other peptides, and its use as a diagnostic/prognostic marker as well.
Both the gut microbiome studies on LCMS and BNP on MALDI-MS have been done in large cohorts (around 10,000 for the former, and 3,000 for the latter) which have required the instruments to be reliable and reproducible over extended periods of time to undertake the studies. One Shimadzu feature that I highly appreciate is reliability. As mentioned above, being able to carry out measurements over an extended period of time is absolutely critical to measure thousands of samples as needed for cohort/population studies as part of phenomics activity that my lab has an interest in. Having been involved in the development of the LCMS-8050, reliability and high-speed analysis were critical issues as there was envisioned use for clinical/cohort samples, and will surely remain a defining feature of Shimadzu instruments moving forward.
Finding Novel Biomarkers for Heart Failure
Helen Jordan, PhD candidate at the University of Leicester. Shimadzu UK is the industrial partner for her MRC IMPACT CASE Awards PhD studentship with Prof. Toru Suzuki.
Hi, my name is Helen Jordan and I’m a second-year PhD student at the University of Leicester, working with Professor Toru Suzuki. My PhD is funded by the MRC in partnership with Shimadzu and is titled “Investigating Novel Metabolomic Biomarkers of Heart Failure”. Prior to the disruptions caused by Covid-19, I have visited the Shimadzu office in Milton Keynes and learnt first-hand about their LC-MS equipment.
As a research group, we investigate metabolomic biomarkers of cardiovascular diseases, especially heart failure. My PhD project involves both untargeted and targeted metabolomic studies. Firstly, I hope to gather data from untargeted studies using Shimadzu’s QTOF-9030. This will help me to identify potential metabolites of interest. A metabolite of interest will be any that is found to differ between a heart failure cohort and healthy cohort. Recently, the research group has moved from Glenfield Hospital to a new building on campus where we have access to a Shimadzu LCMS-8060. On the LCMS-8060, I will be able to carry out my targeted metabolomic studies, validating potential biomarkers of heart failure from untargeted studies in a clinical cohort. The success of the biomarker will be established based on its ability to correctly separate the heart failure cohort from the healthy cohort.
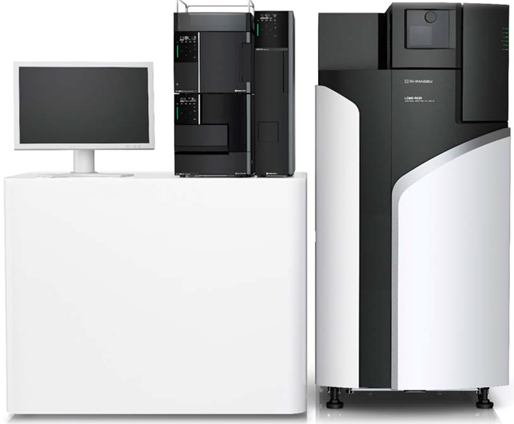

QTOF-9030
Ultimately, the aim of this project is to improve knowledge of diagnostic biomarkers. This will hopefully contribute to more accurate diagnosis in a clinical setting.
When I was asked to name my favourite Shimadzu feature, I decided to name their Technical Support team Chris Titman and Christine Hinz. Besides sharing their wealth of knowledge, they have both offered a lot of support in what has been a difficult year to be a PhD student. They have filled me with confidence that we will produce quality data and eventually an entire thesis! I cannot thank them enough.
Simplifying Clinical Samples Analysis using a Fully Automated CLAM-LC-MS/MS Approach
Emmanuelle Braidman, Shimadzu collaboration with Health Service Laboratories (HSL) in London to “make the CLAM-LC-MS/MS the system of choice for clinical laboratories around the UK.”
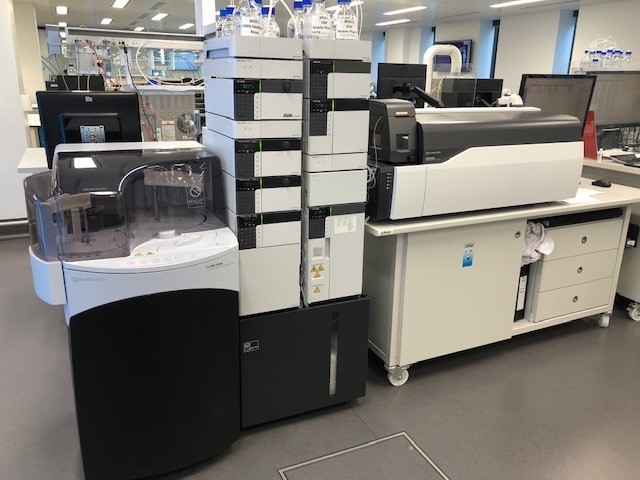

CLAM and LCMS-8050.
Quantitative steroid measurement in serum is essential for the diagnosis and monitoring of adrenocortical (e.g. congenital adrenal hyperplasia, Cushing’s syndrome, primary aldosteronism) and gonadal pathologies. As they are involved in many physiological processes, steroids are important biomarkers to assess health status and to investigate environmental effects on exposed populations. In paediatric or post-menopausal samples, circulating levels of reproductive hormones are very low and therefore challenging to measure. In addition, sample volume availability can be limited adding difficulties for high-sensitivity analysis.
Historically, the measurement of serum steroids has been performed by immunoassay or GC-MS; both of which have well recognised limitations. Immunoassays are renowned for their low analytical specificity due to matrix effects and interferences from closely related compounds, whereas GC-MS analysis requires labour intensive and time-consuming sample preparation involving SPE or Liquid-Liquid extraction with derivatisation.
One of the projects currently undertaken in collaboration with HSL laboratory is aiming to develop and validate a selective LC-MS/MS method for steroids panel analysis in serum while reducing sample preparation to a minimum with little human intervention. The instrument used for this new project is LCMS-8050 placed in line with the CLAM system. The CLAM is a fully automated sample preparation module for LC-MS/MS. A simple protein precipitation followed by filtration can be programmed on the CLAM.
Sample preparation is synchronized with the LC-MS/MS system allowing good sample extraction reproducibility with no loss of time. 4 steroids of diagnostic importance (DHEAS, Testosterone, 17-OHP and Androstenedione) investigated using 2 specific MRM transitions each. MRM transitions were determined on the LC-MS/MS using the automated MRM optimization tool with precision. This is a key feature of Shimadzu LC-MS/MS instruments that facilitate the creation of MRM methods. The use of LabSolutions Insight software is also easing the workflow process in terms of data reviewing.
A second project on this system is to develop and validate a method that will allow the determination of urinary free cortisol and cortisone to add a new dimension to the diagnostic of Cushing’s syndrome. The objective is to create an analytical method that will allow the improvement of the sample throughput within the laboratory by reducing the sample preparation and analysis times with the possibility of 24hours batches extraction-analysis. Those two projects are also a good opportunity to support clinical staff to understand and use with confidence the Shimadzu instrumentation.
International Customer Interviews
Dr Adam Cawley, Science Manager, Australian Racing Forensic Laboratory, Racing NSW. Equine Anti-Doping; a Multidisciplinary Field Involving Chemistry, Biology, Pharmacology and Veterinary Science.
For routine target-based methods and metabolomics research the LCMS-9030 has demonstrated:
a. Speed – genuine 100 Hz for Data Independent Acquisition (DIA).
b. Stability – ≤ 2 ppm mass accuracy from a single calibration performed over 2 weeks.
c. Collision Energy (CE) spread function to obtain MS/MS spectra at nominated and ± CE range.
More generally, my laboratory chooses Shimadzu equipment due to the excellent post-sales support provided. The availability of experienced applications and service engineer personnel, without the requirement for expensive contracts, sets Shimadzu apart from a customer perspective.

Dr Cawley and the LCMS-9030
Shimadzu LCMS and MALDI customers receive global advertisement via various media, such as Analytical Scientist, Institute of Biomedical Science, on-going social media promotion and many more. Find the full interview here: User interviews : SHIMADZU (Shimadzu Corporation)
Analytical Intelligence (AI) Designed to Increase Efficiency and Improve Workflows
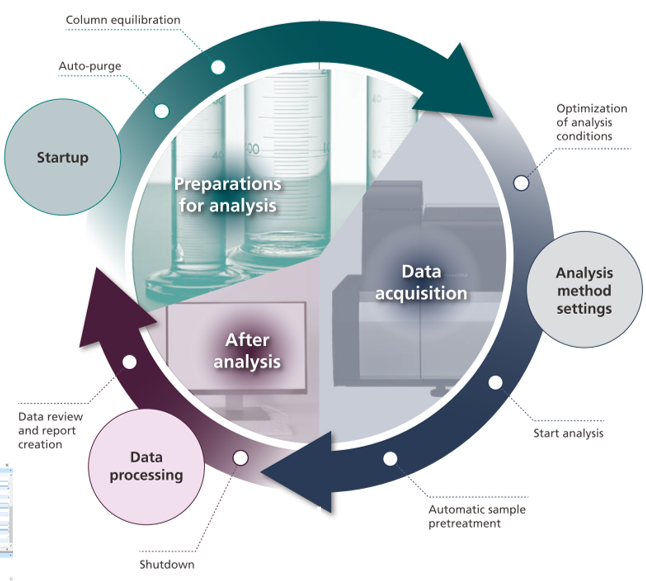
Efficient workflow with analytical intelligence assistance
Shimadzu is an innovative and forward-thinking company with the goal to help our customers succeed and make the experience of sample analysis as smooth, efficient and reliable as possible. We push analytical boundaries with our hardware development by employing analytical intelligence (AI) to improve analysis workflows and make them more efficient which is highly important in our demanding, fast pace world. Recent software developments also provide intelligent automated processes which can improve the analytical workflow and productivity. From automated start-up functions including auto-purge and column warm-up methods, solvent monitoring, automated MRM and ion source optimisation using Connect, intelligent batch creation, automated instrument shutdown to efficient data review in Insight, our instrumentation and software make your analysis an enjoyable experience.
We live in a continuously evolving environment where new challenges and revised regulations enter our lives all the time. A new contaminant or impurity is identified, or your robust and reliable assay suddenly must address revised reporting levels. If these events push your technology beyond its capabilities, you are looking at new capital expenditure.
With Shimadzu LC-MS/MS you have another option. These systems offer an upgrade path, which allows users to field upgrade their LC-MS/MS to higher specification models.
In addition, we have ensured that users have the flexibility to upgrade right up to our new market leading LCMS-8060NX.
This has the benefit of saving you time and money, whilst increasing your return on investment and it protects the environment by reducing the impact of manufacturing and transporting new systems. It also enhances your professional credibility - getting budget approval for a system upgrade is often simpler to achieve, rather than a much larger expenditure for an entirely new instrument.

Connect
Our MRM optimisation tool previously found in our acquisition software has been redefined: Connect allows for automated optimisation of MRM parameters (precursor and product ion m/z, voltages) and ion source parameters (gas flow rate, temperature). This all-round comprehensive, automated optimisation maximises sensitivity by taking into consideration polarity, adduct ions and charge numbers etc.
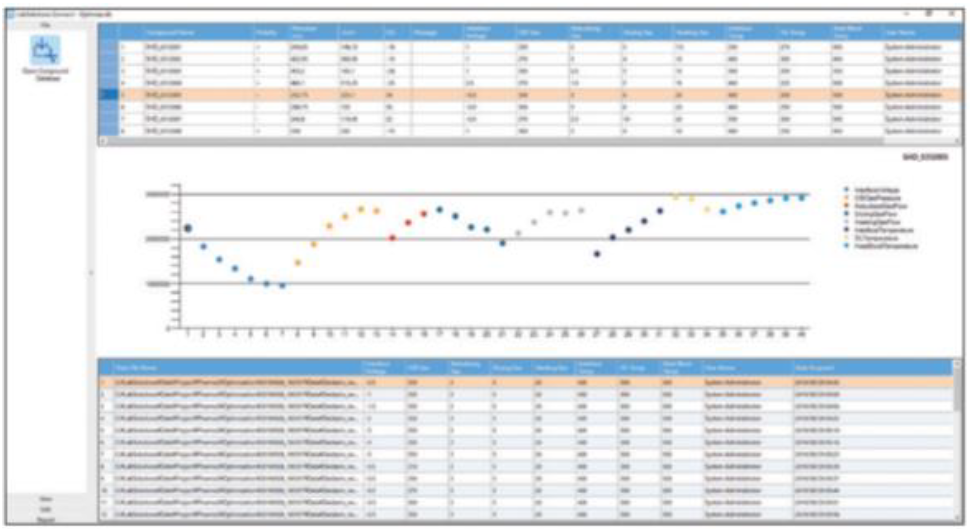
Ion source parameter optimisation displays the successive results of each parameter modification.
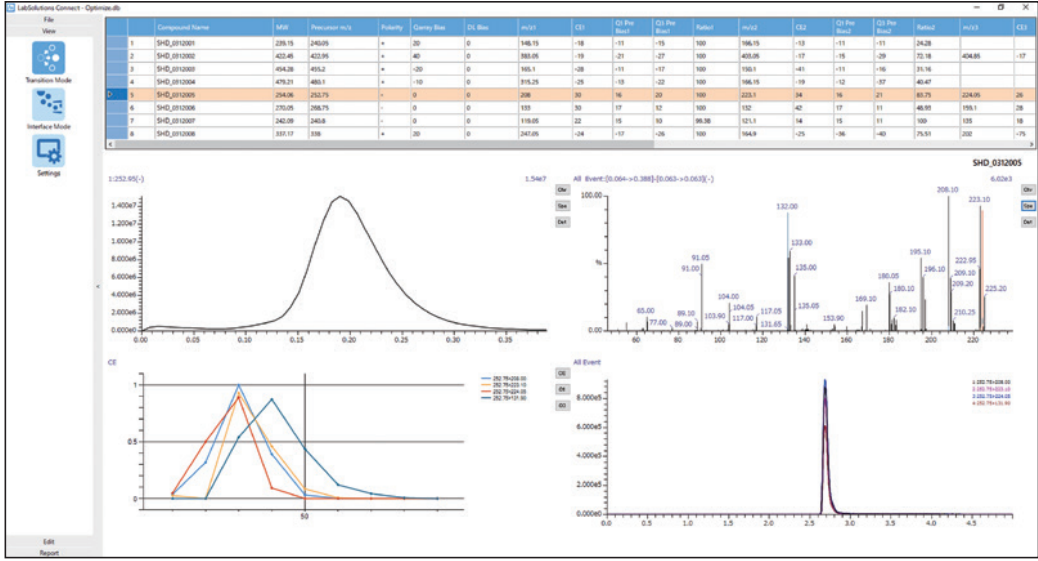
MRM optimisation displaying precursor and product ion m/z as well as voltage results simultaneously.
For efficient data review, results are both graphically visualised and listed in table format. Changes to signal intensity due to instrument parameters variations can also be followed in the chromatogram, spectrum or intensity charts, which can all be displayed in a single window for quick and easy data review.
Using Connect MRM libraries can be easily built allowing for more efficient method development.