LabSolutions CS Video
HPLC Troubleshooting Course
6 - Changes in Peak Shape - Part 2
8 - Peak Area Fluctuations
9 - Retention Time Fluctuations - Part 1
10 - Retention Time Fluctuations - Part 2
11 - Column Lifespan - Part 1
12 - Column Lifespan - Part 2
13 - Detector Issues
14 - Flow Line Leakage
15 - Course Summary
In most cases, quantification is achieved using the area of a peak. If the peak area fluctuates due to external influences, it leads to over- or underestimation of the analyte amount - the result does not match reality. In order to achieve consistent and reliable results, in this section we are going to explore aspects around the injection of the sample and temperature of the detector cell.

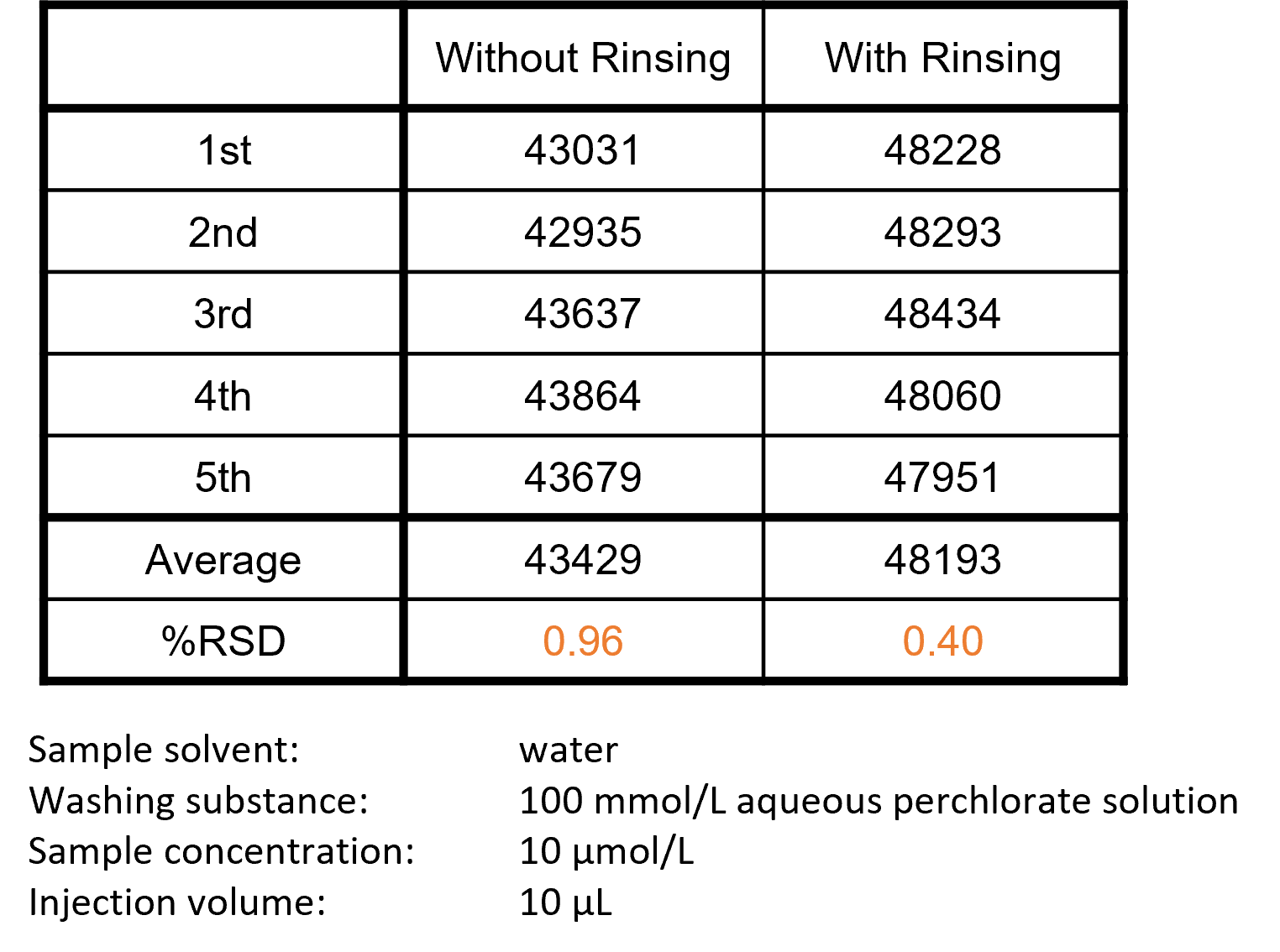
The most common cause of peak area fluctuations is variation in the injection volume. To check for any variation, repeated injections of a reference with a known concentration are recommended (gravimetrically assessed water can be used). Constant conditions should always be maintained, as you can see from the table on the right, even the rinsing of the needle can have a significant impact on the deviation. It is, however, always good practice to ensure that the needle is rinsed between injections to avoid any sample carryover.
For highly viscous samples, the draw speed should be reduced, as air bubbles could otherwise be sucked in which will cause significant variation in the amount of sample that ultimately makes it onto the column.
Air bubbles in the rinse solution or an empty rinse solution can also lead to fluctuations in peak areas. Therefore, it is also recommended that all lines are purged regularly.


As you can see from the table on the right, depending on the substance, different adsorption effects can occur on the injection needle or the seal. Five repeat injections of caffeine and thiamine standards were injected and measured using the same method, but the thiamine shows twice the standard deviation. In this case, the rinse solution of the injector and the pretreatment program should be adjusted to the analytes.
To check repeatability, an adsorption-resistant internal standard should always be used.

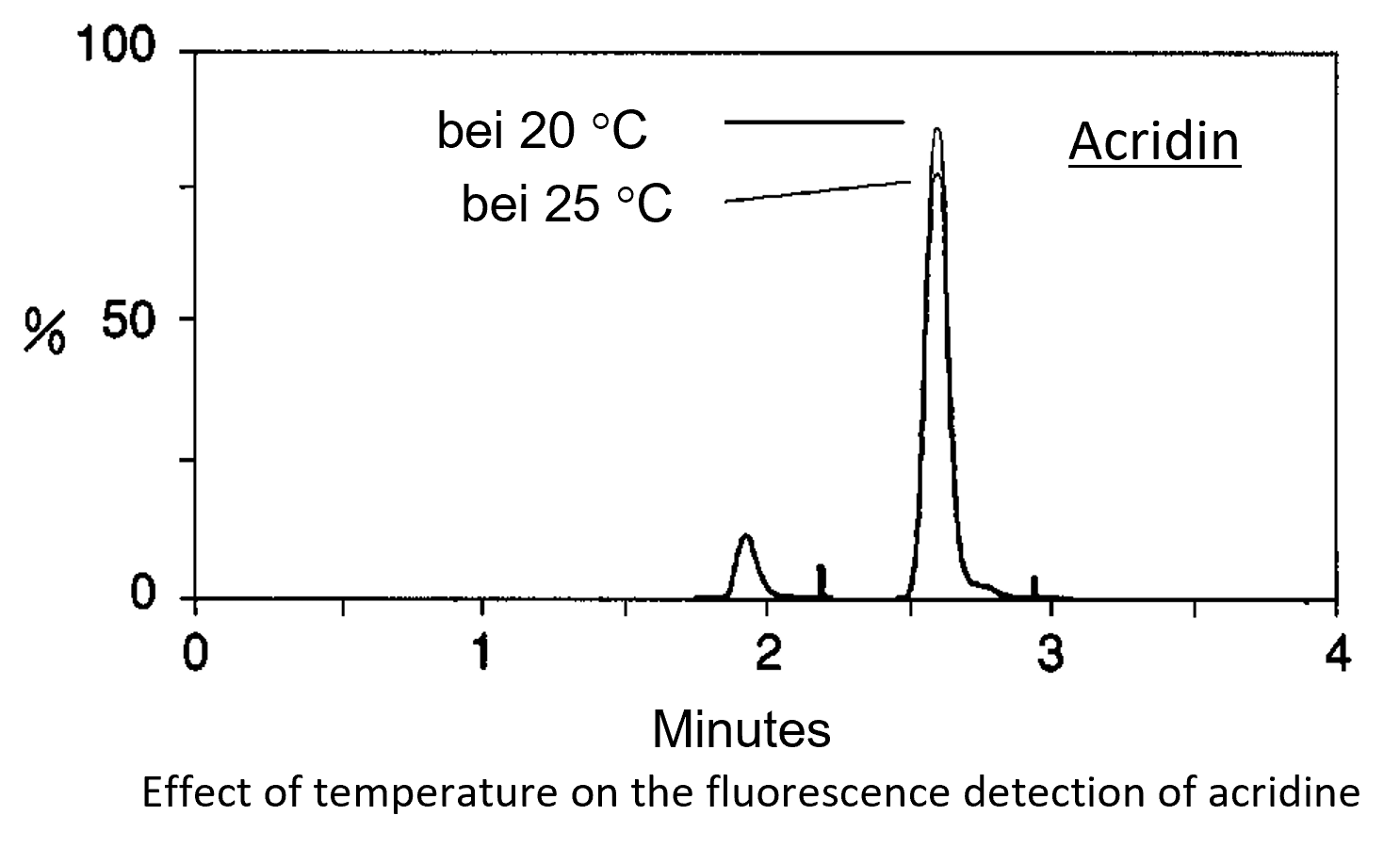
The detection temperature in the measuring cell has a significant impact on the signal. If the temperature fluctuates, the signal also fluctuates in its height. The refractive index detectors is particularly sensitive to temperature changes. However, UV/Vis detectors or fluorescence detectors also react to temperature changes. For example, if the temperature of a fluorescence detector cell increases, the signal decreases. Therefore, temperature control of the detector cells is essential.
Additionally, the room temperature should be kept as constant as possible. The system should not be placed in a draft, directly under an air conditioning unit, or in direct sunlight. As you can see from the image to the right, even a relatively small change in temperature (e.g. lab temperature changes from spring to summer) can impact the result.

Methods of Troubleshooting:
Firstly, you should check the autosampler. If this is not the cause of the peak area fluctuation, the detector should be checked. In rare cases, the adsorption of analytes on the column packing material can be the cause. This is especially the case with ODS columns and basic, chelating substances. Check the suitability of the column used for your analysis. If sufficient information is not found in the column's datasheet, contacting the column manufacturer is recommended.
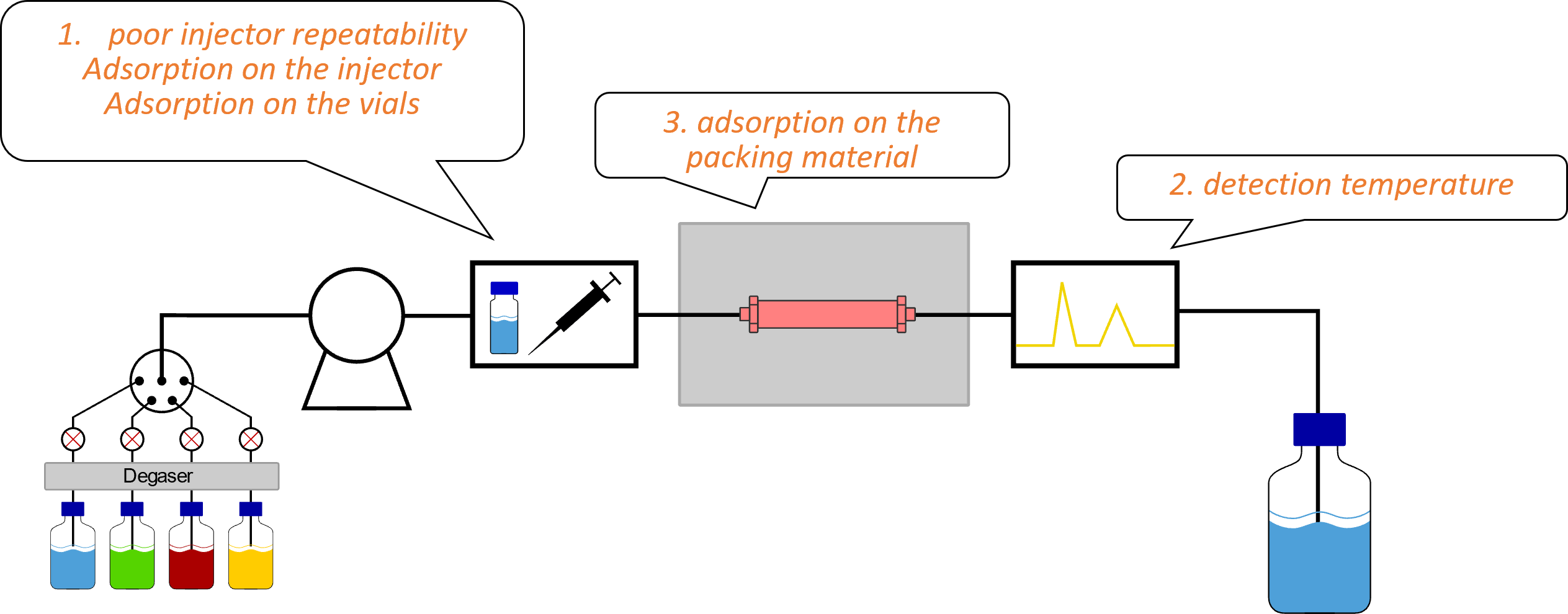

General:
System:
In addition to peak area fluctuations, retention time fluctuations are a common problem. Therefore, the next two parts of the troubleshooting course will address the possible reasons for retention time fluctuations and how they can be resolved.
Your Shimadzu LC Team
LabSolutions CS Video