Ghost Peaks
LCMS Troubleshooting Course
6 - Changes in Peak Shape - Part 2
7 - Ghost Peaks
8 - Peak Area Fluctuations
9 - Baseline Disturbances
10 - Retention Time Fluctuations - Part 1
11 - Retention Time Fluctuations - Part 2
12 - Changes in Chromatographic Resolution
13 - Changes in MS Response
14 - Undesired Fragmentation & Ion Source Settings
15 - Course Summary & Quiz
Ghost Peaks and Carryover
Welcome back to this 7th course unit which is looking at ghost peaks and carryover. Unwanted peaks, typically known as ghost peaks, and carryover can both interfere with accurate data interpretation, especially if they coelute with target analytes or persist between injections. Consequently, avoiding these occurring peaks and those arising from contaminants is a critical aspect of the analysis.
1. Ghost Peaks (Unexpected Peaks in Blanks)
Ghost peaks can significantly interfere with data evaluation and potentially produce false results. They are rarely an issue for targeted MRM type analysis but can be a greater issue for scan analysis.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Contaminated Eluents |
Replace solvent containers regularly, and do not top-up bottles.
Maintain and monitor waste purification systems.
Use a gradient to wash off contaminants which have accumulated at the head of the column.
|
| Incorrect Solvent Quality |
Some LCMS grade solvents may contain UV active contaminants, affecting UV detection. However, they may not ionise in the ion source, therefore it is important to use the right quality solvent
Install a ghost trap which can be replaced if contaminated
Switch solvent batches or manufacturers if ghost peaks persist

Fig. 1 The QArray Skimmer from an LCMS instrument which was using LC grade solvents
|
| Inadequate Column Equilibration / Carryover from Previous Run |
Include post-run rinsing and ensure full equilibration before next injection
This is essential in complex sample matrices to ensure all polarity compounds are eluted from the column
|
| Contaminated Sample Solvent / System Flow Path |
Degas solvents (remove dissolved gases)
Clean flow lines; trapped impurities can elute during gradients
|
2. LCMS Carryover (Residual Signal Between Injections)
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Column Contamination |
Flush column or replace guard column / analytical column if fouling persists.
|
| Injector Issues |
Verify programmed injection volumes
Use a system suitability test to detect injection volumes
Check the batch is programmed for the correct injection volume
Purge the injector metering pump
|
| Inadequate Wash Settings |
Check wash solvent compatibility with analyte
Increase needle and loop flushing cycles

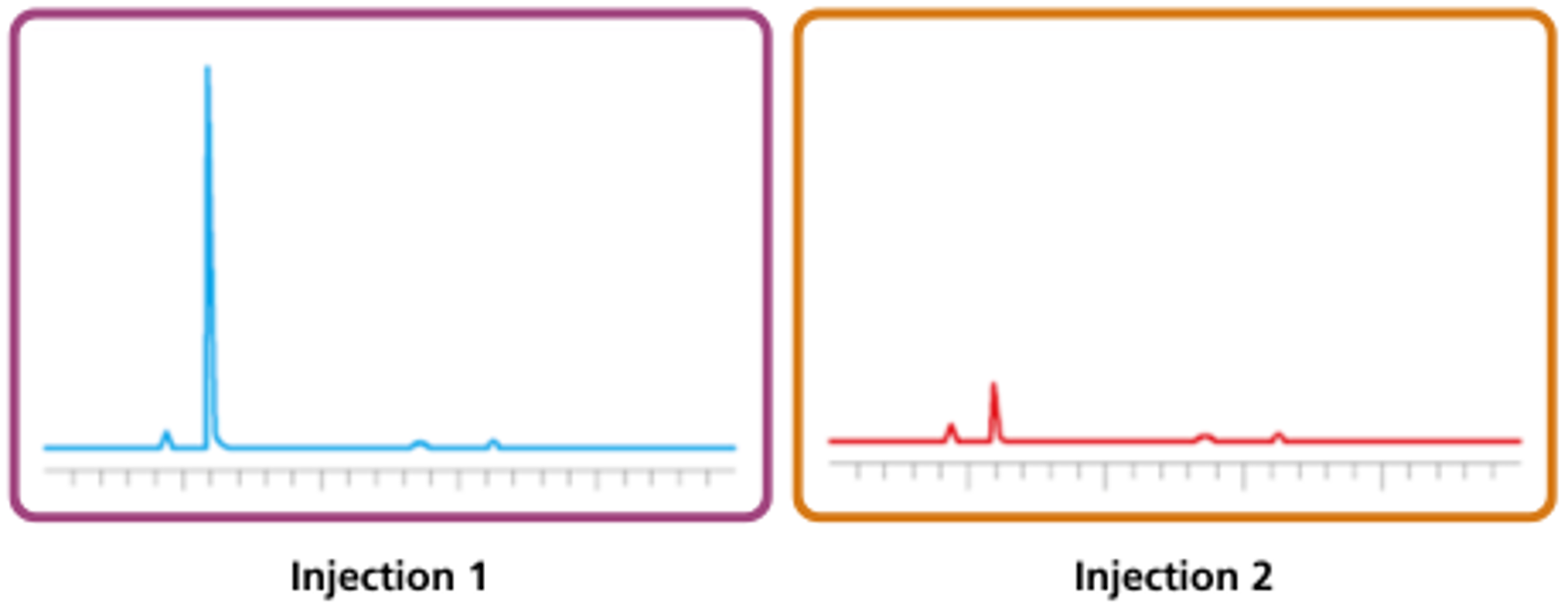
Fig. 2 Minimal carryover when appropriate rinse solvents are used |
| High Sample Concentration / Overload |
Inject smaller sample volumes or dilute samples
|
| Insufficient LC gradient |
Extend the high-strength solvent hold at the end of the gradient to elute strongly hydrophobic compounds
|
3. Extra Peaks
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Other Components in the Sample |
Assess if these peaks are caused by degradation
Prepare fresh samples
Consider the synthetic process which could cause additional analytes to be in the sample
|
| Late Eluting Peaks from Previous Injection |
Increase the run time or solvent strength
Increase the flow rate to increase the number of column volumes in the postrun. Remember to allow for sufficient time to stabilise when returned to the prescribed flow rate.
|
Daily Checklist to Prevent Ghost Peaks & Carryover
Unwanted peaks in the chromatogram are disturbing during evaluation and can deliver false results if they coelute with target analytes. Therefore, attempts are always made to avoid ghost peaks as well as regular peaks from contaminants.

Fig. 3 Common sources of ghost peaks and contamination.
That is all for this week. We hope this has given you some insight into the most common issues surrounding ghost peaks and carryover, and how to mitigate against these problems. Next time, we will be looking at common causes of peak area fluctuations.
Your Shimadzu LCMS Team
Related Resources
-
-
Watch short videos explaining analytical intelligence features of Shimadzu HPLC systems
-