Search Shimadzu's range of HPLC columns to find the right one for your application.
Retention Time Fluctuations (Part 1)
LCMS Troubleshooting Course
6 - Changes in Peak Shape - Part 2
10 - Retention Time Fluctuations - Part 1
11 - Retention Time Fluctuations - Part 2
12 - Changes in Chromatographic Resolution
13 - Changes in MS Response
14 - Undesired Fragmentation & Ion Source Settings
15 - Course Summary & Quiz
Part 1: Temperature Effects, Eluent Composition, and Flow Rate Issues
Retention time is a critical parameter in LC and LCMS, used to identify analytes reliably. They are characteristic of the analyte under certain chromatographic conditions with a specific column, which allows for confidence in analyte identification. Fluctuations can compromise data accuracy, reproducibility, and confidence in analytical results.
This topic is divided into two parts:
- 1. Temperature effects, eluent composition, and flow rate issues.
- 2. Stationary phase, instrument related issues, and best practices.
1. Temperature Effects on Retention Time
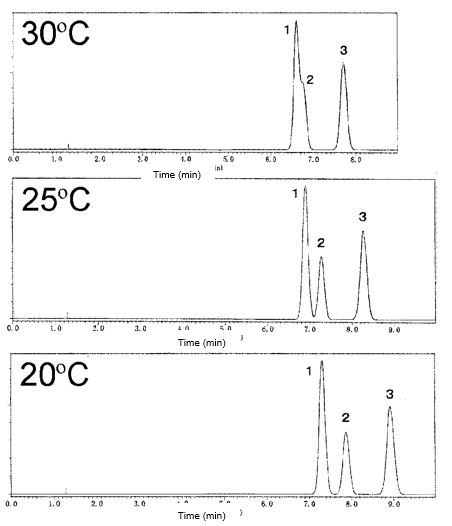
Fig. 1 Movement of peaks based on temperature. 1. Sorbic acid, 2. Benzoic acid, 3. Methylparaben
IMPACT: A 1°C change can shift retention time by 1–2%, most significantly for late-eluting analytes. For example, at 20°C vs. 50°C, runtime nearly halves, but compound resolution may be altered (e.g., sorbic acid and benzoic acid coeluting at 30°C).
Solutions:
2. Flow Rate Variability
IMPACT: Worn piston seals, leaks, or pump inaccuracies can cause retention shifts.
Solutions:
3. Eluent Composition & Equilibration
| Cause | Description | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Inadequate Equilibration | Within reversed phase chromatography, the stationary phase requires sufficient time to create the environment for separation. This requires typically 10 column volumes. When switching between two different mobile phase conditions, such as when replacing the storage solution, the column must be equilibrated. This process takes significantly longer for other modalities such as HILIC, which is typically in excess of 100 column volumes |
Set column equilibration to greater than 10 column volumes
After high organic rinses, ensure sufficient re-equilibration to initial conditions
Insufficient equilibration can lead to progressively shorter retention times or greater variability.
|
| Mobile Phase Preparation Errors | Significant attention should be paid to the mobile phase, as together with the column, the eluents are crucial for the chromatographic separation and stable measurements. Errors in preparation or storage can cause considerable issues for accuracy and reproducibility. |
Use precise, standardised preparation methods (e.g. volumetric flask vs direct mixing). Ensure this is written in a standard operating procedure for others to follow accurately.
Inaccurate solvent ratios can cause inconsistent elution strengths therefore be consistent and precise in how to create solvents
Consider pre-mixed mobile phases for regulated workflows.
|
| Storage & Handling | The solvents should be properly maintained and disposed of in a timely fashion in order to ensure the correct chromatographic results are obtained. |
Keep eluents in sealed bottles, away from the sunlight or drafts.
Use carbon filters on the solvent caps on the instrument to minimise evaporation of solvent
Dispose of solvents in a suitable timeframe, particularly for volatile additives and solvents such as formic acid.
|
This section of the course has provided three common issues which can cause issues for retention time stability. Ensuring the system is performing correctly, the stationary phase is properly equilibrated and the mobile phases are correctly prepared and installed are paramount to improving the reproducibility of your chromatography.
Your Shimadzu LCMS Team
Related Resources
-
-
Watch short videos explaining analytical intelligence features of Shimadzu HPLC systems
-
Learn about our beginnings, dating back to 1875, through to modern day Shimadzu.